The Trunk of a Tree is Its __: A Journey of Discovery
A tree trunk is the main stem of a tree. It is typically composed of wood, but can also be made of other materials such as bamboo or steel. The trunk supports the branches and leaves, and stores water and nutrients.
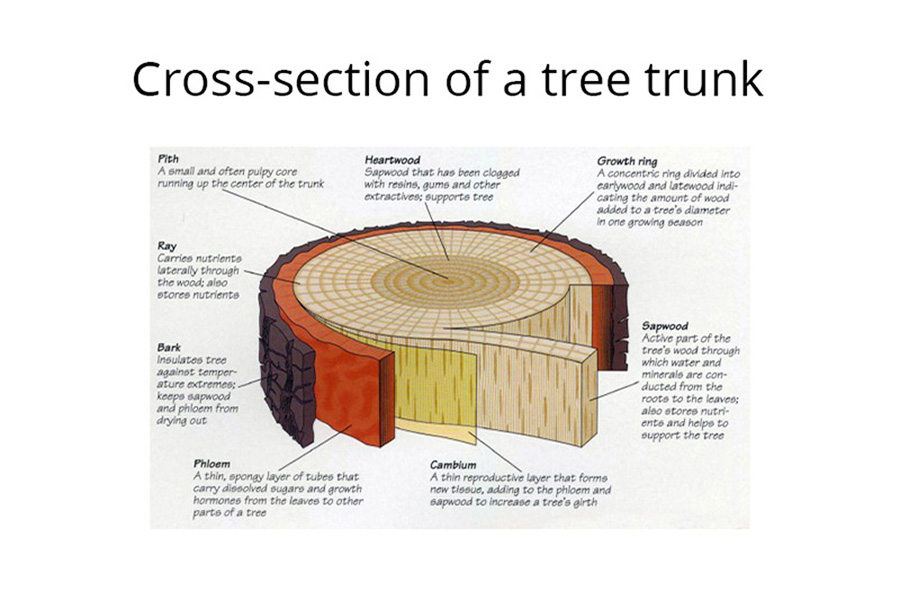
The structure of a tree trunk varies depending on the tree species, but all trunks share some common features. These include the bark, sapwood, heartwood, cambium layer, and xylem and phloem tissue. The function of a tree trunk is to transport water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant and to provide support for the leaves and branches.
Did you know that the anatomy of a tree trunk is quite fascinating? The trunk comprises three main parts – the inner bark, the cambium layer, and the xylem. Each part plays an important role in the overall function and structure of the tree.
The inner bark is the protective layer that covers the cambium layer. The cambium layer produces new cells, which help thicken the trunk as the tree grows. The xylem comprises hollow tubes that transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves.
Each layer plays an important role in keeping the tree healthy and strong. Without a healthy trunk, trees would not be able to survive!
Credit: www.arboristnow.com
What are the Parts of a Tree Trunk And Their Functions?
The tree trunk is the main body of the tree. It consists of the heartwood and sapwood. The heartwood is the innermost layer of the tree trunk and is made up of dead cells.
The sapwood is the outer layer of the tree trunk and is made up of living cells. The bark is the outermost layer of the tree trunk and protects the tree from predators, diseases, and insects.
What is a Tree Trunk Anatomy?
A tree trunk is the main stem of a tree. It is typically cylindrical in shape, tapering slightly towards the top. The trunk is covered in bark, which protects the tree from damage.
Beneath the bark is the xylem, which transports water and nutrients up to the leaves. The phloem transports sugars and other organic molecules down from the leaves. The cambium layer is a thin layer of cells that divide to produce new xylem and phloem cells.
This process of cell division, known as secondary growth, results in an increase in the diameter of the trunk over time. The outermost layer of the trunk is made up of living cells known as the cortex. beneath this is a layer of dead cells known as pith.
Together, these two layers make up the periderm. The periderm helps to protect against water loss and fungal infections.
What is the Anatomy of a Tree?
A tree is a tall and sturdy plant that has a trunk, branches, and leaves. The trunk of a tree is the main body of the tree. It is covered in bark, which protects the tree from insects, diseases, and other damage.
The branches of a tree grow out from the trunk and are where the leaves are located. The leaves of a tree are what gives the tree its food. They use sunlight to make food for the tree through a process called photosynthesis.
What is the Main Function of the Stem Trunk?
The main function of the stem trunk is to support the leaves and flowers. The stem also stores food for the plant and helps transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves.
Lecture 5 Tree Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 Video
Parts of a Tree Trunk And Their Functions
Assuming you would like a blog post discussing the different parts of a tree trunk and their functions: A tree trunk is mostly made up of wood, which is composed of xylem tissue. Xylem tissue is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to the leaves.
The cells that make up this type of tissue are elongated and have thick walls. In addition to wood, tree trunks also contain phloem tissue. Phloem tissue transports food (in the form of glucose) from the leaves to the rest of the tree.
The cells that makeup phloem tissue are shorter than those in xylem tissue and have thinner walls. The bark is the outermost layer of a tree trunk. Its main function is to protect the inner layers from damage.
The bark also helps regulate temperature and store water. Underneath the bark is the cambium layer, which is made up of living cells that divide and grow to add new layers of xylem and phloem tissues. The heartwood is the central part of the tree trunk that contains no living cells.
It provides support for the tree and gives it strength. The sapwood is the outer part of the heartwood that contains living cells.
What is the Function of the Trunk of a Tree
A tree’s trunk functions as the tree’s primary support system. It is responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and also provides structural support for the branches and leaves. The bark of the trunk protects the tree from damage by insects, animals, and weather.
The wood of the trunk is used in construction, furniture making, and other woodworking projects.
What is the Function of the Outer Bark of a Tree
The function of the outer bark of a tree is to protect the tree’s inner layers from damage. The outer bark is made up of dead cells constantly replaced by new cells. This process is called exfoliation, and it helps keep the tree healthy by allowing nutrients and water to reach the tree’s inner layers.
The outer bark also provides insulation for the tree, helping to regulate temperature and prevent moisture loss.
What are the Five Parts of a Tree
When it comes to trees, there are five main parts that you need to be aware of. These include the roots, trunk, branches, leaves, and flowers. Each part plays an important role in a tree’s life and our planet’s ecology.
Here’s a closer look at each part:
- Roots: The roots of a tree anchor it into the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Roots also store food for the tree and help to support its weight.
- Trunk: The trunk is the tree’s main stem that supports the branches and leaves. Trunks can be either straight or curved, depending on the species of tree.
- Branches: Branches grow out from the trunk and provide support for leaves. They also produce buds which give rise to new leaves and branches.
- Leaves: Leaves are flattened structures containing chloroplasts that allow them to perform photosynthesis – a process that produces food for the tree. Leaves come in many shapes and sizes depending on the tree species. Some trees (such as deciduous trees) lose their leaves during autumn while others (like evergreen trees) keep their leaves all year round.
- Flowers: Flowers are reproductive organs that produce seeds for new plants.
What is the Bottom of a Tree Called
The bottom of a tree is called the root system. The roots are typically underground, but they can also be aerial (growing above ground) or adventitious (growing on other surfaces). The primary function of roots is to anchor the tree and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
However, roots also play an important role in storing carbohydrates and producing hormones that help regulate plant growth. There are many different types of root systems, but they all have one thing in common: they must be able to support the weight of the tree above ground. This means that roots typically grow much larger and thicker than other parts of the plant.
The largest root systems are found in tropical forests, where trees can grow up to 100 meters tall! The bottom of a tree’s trunk is called the buttress root system. This type of root system is often found in rainforests, where it helps stabilize trees against high winds and heavy rains.
Buttress roots are typically large and flat, growing outwards from the trunk at a 90-degree angle. Some buttress root systems can be as large as 30 meters wide!
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the trunk of a tree answer?
The trunk of a tree is its main stem, typically upright and woody, that supports branches and leaves.
Is a tree trunk a branch?
No, a tree trunk is not a branch. The trunk is the main, central part of a tree that supports the branches and leaves, while branches are smaller stems that extend from the trunk.
What is the trunk also known as?
The trunk of a tree is also known as the “main stem” or simply the “stem” of the tree.
Conclusion
A tree trunk is the main stem of a tree. It supports the branches, leaves, and fruit of the tree. The trunk is made up of three parts: the inner bark, the cambium, and the outer bark.
The inner bark is the living tissue that transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the tree. The cambium is a layer of cells that produce new growth in trees. The outer bark is the protective layer that covers the trunk.
The structure of a tree trunk helps it to perform its functions. The inner bark transports water and nutrients from the roots to other parts of the tree. The cambium produces new growth in trees. The outer bark protects against damage and pests.
Related Articles:
10 Best Small Evergreen Trees with Non Invasive Roots
 Dr Ahsanur Rahman, PHD
Dr Ahsanur Rahman, PHDPine Tree Rescue: Saving Pine Trees with Brown Needles
 Dr Ahsanur Rahman, PHD
Dr Ahsanur Rahman, PHD





